Project Title:
Creation of a flexible methodology for development and management of innovative projects in scientific organizations
Funding: National Science Fund, Competition for financial support for basic research projects on societal challenges – 2018 Duration: 36 months Start Date: December 2018 Beneficiary: UNWE Project Coordinator from IICT-BAS: Assoc. Prof. Nikolay Stoimenov, Ph.D.Abstract: The project aims at creating a flexible methodology for development and management of innovative projects in scientific organizations (FMIPSO), based on the flexible methodologies: Lean startup, Agile, Scrum, Design thinking, User centricity and User innovation. The creation of FMIPSO addresses the weak success of the developed and realized innovations by Bulgarian scientific organizations. This problem directly influences the last position of Bulgaria in a numerous of indices and ratings, assessing innovation performance, innovation progress and performance (European Innovation Scoreboard, Bulgarian National Statistical Institute, Innovation.bg, Eurostat, World Bank, Global Innovation Scoreboard , The World Economic Forum, the Global Competitiveness Report, Innovation and the Organization for Economic Mutual Assistance and Development - OECD). This lack of good innovation performance by scientific organizations further increases the distance and integrity of the science-business-related innovation industry.
For the purpose of the testing and creating the final version of the flexible methodology, divergent scientific innovative sub-projects have been selected as a principle of the choice were: high multidisciplinary; scientists interested in developing innovation; specific research projects to develop innovations that are shaped as work packages in the current project to overcome a societal challenge such as increasing competitiveness and productivity of the economy in line with the ISIS areas. The sub-projects that will be carried out within the project will not only be used for comprehensive and in-depth aprobation of the developed FMIPSO but they also meet the societal challenges of the competition recommendations and the priorities of ISIS. These are:
- • "Innovative method for 3D presentation of plane culturally-historical sites by tactile plates for the disadvantaged users
(low sighted or visually impaired people)" - Technical sciences, Institute of Information and Communication Technologies at BAS;
- • "Detection of mutations in the EGFR gene in invasive urinary bladder tumors" - Medical Sciences, Medical University-Sofia,
Medical Faculty, Department of Medical Genetics;
- • "Diagnostics, condition assessment and analysis of reinforced concrete elements" - Technical Sciences, Institute of Information and Communication
Technologies at BAS with the participation of scientists from University of Structural Engineering & Architecture
Part of the young scientists know each other of their visit in Joint Research Center (JRC) in Ispra, Italy, which took place in the period 27-29 June 2018. The selection for the visit of young scientists was made by the Ministry of Education and Science, requiring them to be finalists in the competitions of the National Scientific Fund, Bulgarian Academy of Science and Club Young Talents. After realizing one of the main concepts of the JRC for interdisciplinary research and innovation in each of the various fields, some of us have decided to realize this idea with this project.
As a result of the scientific project, the team pursues the overall goal of increasing innovation from scientific organizations significantly. For dimensions of this innovation growth, the team has the following dimensions: number of innovations; level of novelty of innovation; level of consumer interest in the innovations developed by research organizations; adaptability of innovations developed for technological innovation; adaptability of innovations developed for transfer to other sectors and directions; management skills and processes in the innovation process; direct and accessible relationship scientific organization-business organizations; a level of quality improvement of the current state of the problem that innovation permits; diversifying and opening up the process of innovation in the direction of - open innovation and innovation development network.
Project Title:
3D Digitalization of Objects from National Cultural-Historical Heritage.
Funding: : National Science Fund, Competition for financial support for research projects – 2017. Duration: 36 months Start Date: December 2017 Beneficiary: IICT-BAS, Project Coordinator from IICT-BAS: Prof. Dr. Dimitar Karastoyanov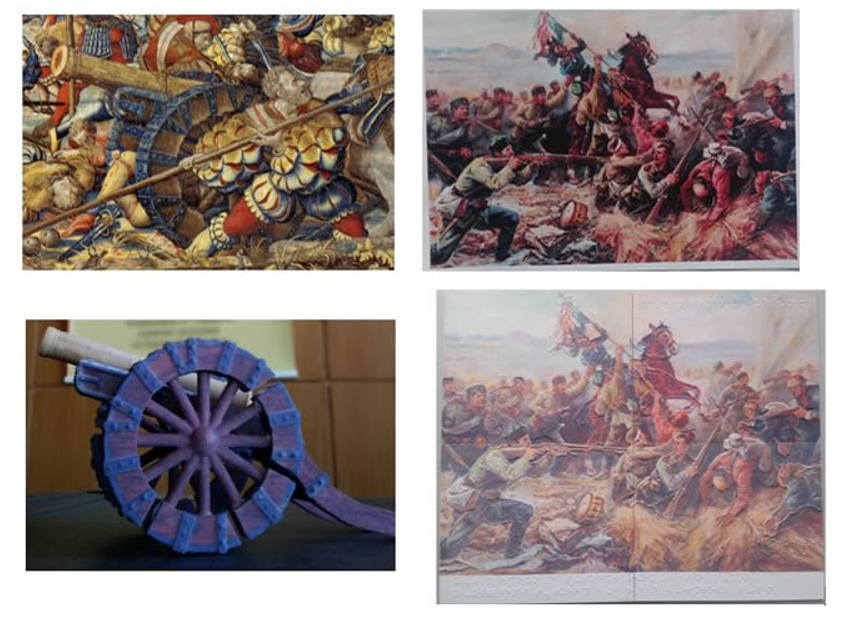
Abstract: in recent years, museums have welcomed millions of visitors to their galleries and exhibitions. However, museums have made little progress towards a concrete understanding of what visitors actually see when they look at works of art. While the impact on some visitors is very strong, the average visitor stops at less than half the exhibits and spends less than 30 seconds on individual artifacts ‒ in most cases, much less.
Another important aspect is by using the possibilities of the information and communication technologies to provide access to the cultural and historical heritage objects for people with disadvantages (for example visually impaired or blind people) so that they can also "see" by touching with their fingers and hands. This will provide them better understanding the relevant presented object – painting, flag, etc.
Also, the results of the proposed project will give the opportunity to a wide range of users to meet the art in a closer way - with 3D models of unique and valuable cultural and historical artifacts that are now kept in vaults for security reasons and this treasures are inaccessible.
Until now, there has been almost no experience in 3D digitization of cultural and historical heritage, especially for disadvantaged people (visually impaired). In the world the ICT's main achievements in this area are mostly implemented in a assistive graphical user interface for people with visual impairments, so they can use computers (Windows icons, etc.).
Objects of the project are to build 3D models of scenes from the national cultural and historical heritage by extracting images from 2D sources - pictures, paintings, engravings. In the presented task, at first place must be modelled a 3D representation of the historical battles of the “Shipka Epopee” - August 1877, in connection with the upcoming celebrations in 2017 and 2018, as well as the presentation of results on the date of the National Day March 3, 2018, Related to possible foreign high level delegations for the celebration, the Bulgarian EU Presidency in 2018 and others.
Separately, the battle for the Samara flag near Stara Zagora and the feat of Lieutenant Colonel Kalitin will be presented, as well as by 3D scanning with an available 3D scanner of nowadays presentations of the relic near Stara Zagora. For visually impaired people, 3D representation of different photos, paintings and scenes with additional alphabet of Braille inside the contours of the figures. Thus, people with visual impairment by touch will be able to "present" the picture, "see" it and "read it".
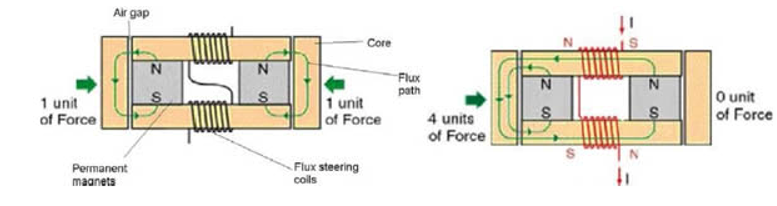
Project Title:
Hybrid electromagnetic systems with magnetic modulation.
Funding: National Science Fund, Competition for financial support for research projects – 2017. Duration: 36 months Starting date: December 2017 Beneficiary Organization: TU-Sofia Project Coordinator: Prof. Dr. Ivan Yatchev Partner Organization: IICT-BAS, Project Coordinator from IICT: Prof. Dr. Dimitar Karastoyanov